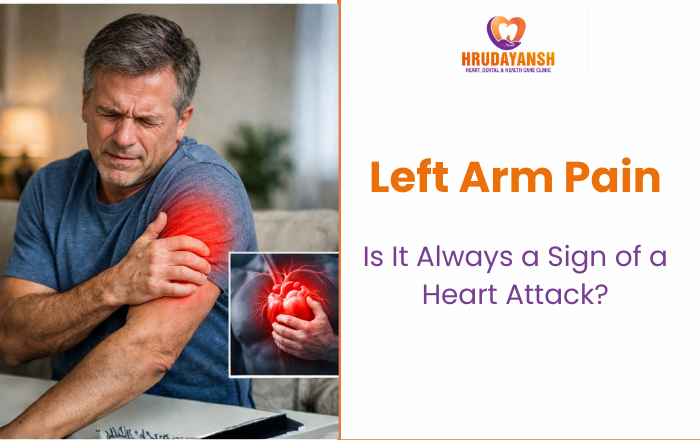
You’re relaxing at home when suddenly your left arm starts aching. No warning. No obvious reason. And your mind immediately races to one terrifying thought — Is this a heart attack?
It’s one of the most common health fears people have — and honestly, it makes sense. We’ve all heard that left arm pain is a classic heart attack symptom. But here’s what most people don’t know: left arm pain doesn’t always point to your heart. In fact, it has several causes — some serious, some not so much.
Let’s break it all down so you know exactly when to worry and when to breathe easy.
Is Left Arm Pain Always a Sign of a Heart Attack?
The short answer? No — but it can be.
Left arm pain is one of several symptoms that may appear during a heart attack, but it’s rarely the only sign. The tricky part is that left arm pain causes range from a pulled muscle to a pinched nerve to something genuinely cardiac. Knowing the difference could save your life.
What Does Heart Attack Arm Pain Actually Feel Like?
During a heart attack, your heart muscle isn’t getting enough blood. Your brain gets confused about where the pain is coming from and sends signals to the left arm, shoulder, or jaw. This is called referred pain.
Left arm pain heart attack symptoms typically feel:
- Dull, heavy, or like pressure — not a sharp, stabbing pain
- Like it’s radiating from your chest down your arm
- Sudden and comes out of nowhere
- Hard to pinpoint to one exact spot
The key thing to remember — cardiac left arm pain almost never shows up alone. It brings company.
7 Warning Signs Your Left Arm Pain Could Be a Heart Attack
Call emergency services immediately if your left arm pain comes with any of these:
- Chest tightness or pressure — even mild
- Shortness of breath
- Cold sweats without physical activity
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness or feeling faint
- Pain spreading to the jaw, neck, or back
- Sudden, crushing fatigue
According to the American Heart Association, nearly 800,000 people suffer a heart attack every year in the US alone — and many dismiss their early symptoms as “nothing serious.”
If two or more of these symptoms appear together with left arm pain — don’t wait. Get help immediately.
6 Other Common Causes of Left Arm Pain (Not Heart-Related)
Here’s the good news. Most cases of left arm pain without chest pain are not cardiac at all. Here are the most common causes:
1. Muscle Strain Overworking your arm, lifting something heavy, or sleeping in a bad position can cause a dull ache in the left arm. This pain usually worsens when you move or press on the area — unlike cardiac pain.
2. Pinched Nerve (Cervical Radiculopathy) A compressed nerve in your neck can shoot pain, numbness, or tingling straight down your left arm. This is one of the most common causes of left arm pain and tingling and is often linked to poor posture or a spine issue.
3. Shoulder Problems Rotator cuff injuries, frozen shoulder, or shoulder bursitis frequently cause pain that travels down the arm. Movement makes it worse — that’s your clue it’s not the heart.
4. Anxiety and Panic Attacks Yes, anxiety causes real physical pain. Muscle tension, fast breathing, and nerve sensitivity during a panic attack can all produce left arm pain that feels shockingly similar to a heart attack.
5. Angina This one is cardiac — but it’s not a heart attack. Angina is chest and arm pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart during activity. It’s a serious warning sign that needs medical attention.
6. Costochondritis Inflammation of the cartilage between your ribs can cause chest and arm pain. It’s usually sharp, gets worse when you press on the chest, and is completely non-cardiac — but it mimics one convincingly.
Left Arm Pain in Women — Why It’s Frequently Missed
Women experience heart attack symptoms differently — and this leads to dangerous delays in treatment.
While men often feel the “classic” chest-crushing pain, women more commonly experience fatigue, jaw pain, nausea, and mild left arm discomfort that’s easy to brush off.
Research published in Circulation found that women are 7 times more likely to be misdiagnosed during an actual heart attack.
Women — please don’t dismiss what your body is telling you. If something feels off, get it checked.
Heart Attack Arm Pain vs. Muscle Pain — Quick Comparison
| Heart Attack | Muscle/Nerve Pain | |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Sudden | Gradual or after activity |
| Feel | Dull, heavy | Sharp, localized |
| Worse with movement? | No | Yes |
| Other symptoms? | Yes | Rarely |
| Location | Radiates from chest | Specific spot |
When Should You See a Doctor for Left Arm Pain?
Go to the ER immediately if:
- Left arm pain starts suddenly with no clear reason
- You have risk factors — high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking history, or a family history of heart disease
- Symptoms don’t go away after a few minutes
See a doctor within 24–48 hours if:
- Pain is mild, linked to movement, and feels muscular
- No other symptoms are present
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Can left arm pain happen without chest pain during a heart attack?
Yes. Some people especially women and diabetics — experience left arm pain without chest pain as their only heart attack symptom.
Q2. Can a pinched nerve feel like a heart attack? Absolutely. Cervical radiculopathy is one of the top conditions mistaken for cardiac pain. An ECG and blood test can tell them apart quickly.
Q3. How long does heart attack arm pain last? It typically persists or comes in waves and doesn’t improve with rest or massage the way muscle pain does. If it lasts more than 5 minutes — treat it as an emergency.
Q4. Can anxiety cause left arm pain?
Yes — muscle tension and nerve sensitivity during anxiety or panic attacks can cause real left arm pain and tingling.
Talk to Dr. Digvijay Nalawade — Cardiologist at Hrudayansh Clinic, Baner, Pune
If you’re in Pune and worried about left arm pain, chest discomfort, or your heart health in general, reach out to Dr. Digvijay Nalawade a trusted heart specialist in Baner at Hrudayansh Clinic.
Dr. Nalawade helps patients understand their heart health clearly, identify risks early, and get the right treatment at the right time.
Your heart works every second of every day. Give it the attention it deserves — book your consultation with a trusted heart specialist in Baner at Hrudayansh Clinic today.